[OS] mount() 시스템 콜 분석
linux kernel sourse tree의 깃허브 코드를 참조해 시스템 콜 호출 시 변화 과정을 분석한 글입니다.
📌 mount()
- 파일 시스템을 지정된 디렉터리 (마운트 포인트)에 연결하는 작업을 수행하는 함수
- 운영체제가 파일 시스템의 데이터를 디렉터리 트리 구조에 통합하도록 함
🫧 과정
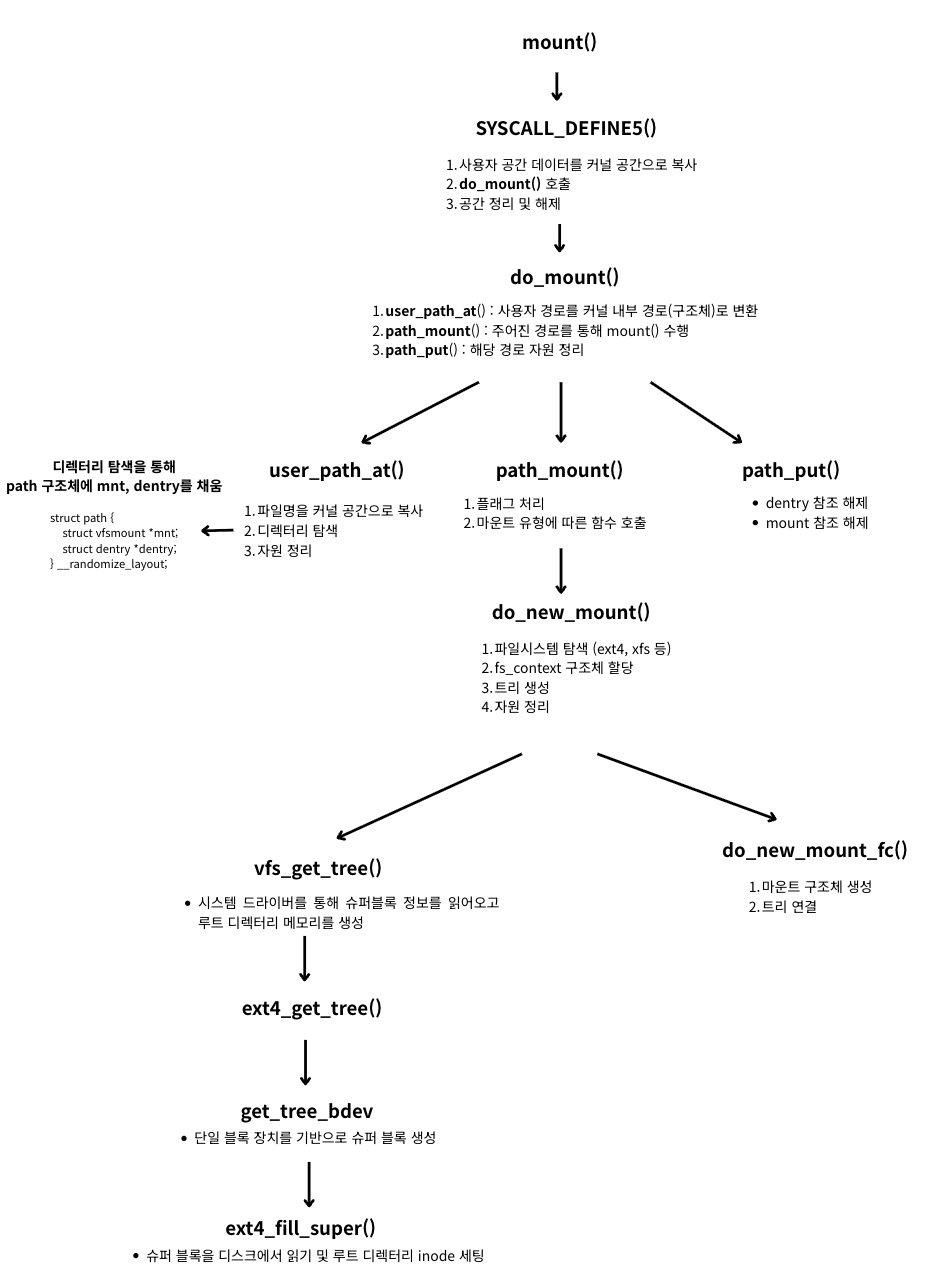
- 시스템 콜을 통해 mount() 요청
- 파일 시스템 파악 후 시스템 드라이버에서 마운트 함수 호출 (이때 빈 슈퍼 블록 구조체도 함께 넘김)
- 드라이버는 디스크에서 슈퍼 블록 드라이버를 읽음
- 읽어온 정보를 빈 슈퍼 블록 구조체에 기입해 리턴
🫧 특징
- 슈퍼 블록 : 파일 시스템의 전체적인 메타데이터가 담긴 디스크 구조
- 커널은 이를 메모리로 로드해야 mount 가능
- 디렉터리 탐색 과정에서 RCU 알고리즘 사용 (lock-free) ⇒ 가시성 보장 X
- RCU로 lock-free 탐색 (읽는 쪽의 데이터 일관성 유지)
- 컨텍스트 스위치, Dentry 구조 변경 등의 이유로 실패 가능
- 락 기반 일반 탐색
- 캐시가 유효하지 않은 경우 디스크에서 재확인
- 디스크 I/O를 줄이기 위해 경로 정보를 dentry cache에 저장해두고 가져다 씀
- RCU로 lock-free 탐색 (읽는 쪽의 데이터 일관성 유지)
✨ 마운트 유형
- 바인드 마운트(MS_BIND) : 이미 존재하는 경로를 다른 위치에서 또 접근할 수 있게 하는 것
- 새 파일 시스템 마운트가 아닌 경로 복붙 느낌으로 사용
- inode가 공유됨
- 리마운트(MS_REMOUNT) : 기존에 마운트된 파일 시스템의 속성을 바꾸는 것
- 실제 슈퍼블록을 언마운트하지 않고 설정만 변경
- 바인드 + 리마운트
- 바인딩된 마운트에 옵션 변경 시 사용
- 이동 (MS_MOVE) : 이미 마운트된 파일 시스템을 다른 디렉터리 위치로 옮김
- 실제 마운트 트리의 연결 지점을 바꾸고자 할 때 사용
🫧 사용 예시 (코드)
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/mount.h>
#include <errno.h>
int main() {
const char *source = "/dev/sdb1"; // 마운트할 장치 경로
const char *target = "/mnt/mydisk"; // 마운트 포인트
const char *filesystemtype = "ext4"; // 파일 시스템 유형
unsigned long mountflags = 0; // 기본 플래그
const void *data = NULL; // 추가 데이터 없음
if (mount(source, target, filesystemtype, mountflags, data) == 0) {
printf("파일 시스템이 성공적으로 마운트되었습니다.\n");
} else {
perror("mount 실패");
}
return 0;
}
🫧 코드
✨ SYSCALL_DEFINE5
- 시스템 콜 인자를 do_mount()로 넘김
- fs/namespace.c, $4040
// 마운트할 장치 경로, 마운트포인트, 파일 시스템 유형, 기본 플래그, 추가 데이터
SYSCALL_DEFINE5(mount, char __user *, dev_name, char __user *, dir_name,
char __user *, type, unsigned long, flags, void __user *, data)
{
int ret;
char *kernel_type;
char *kernel_dev;
void *options;
// 1. 사용자 공간 데이터를 커널 공간으로 복사
kernel_type = copy_mount_string(type);
ret = PTR_ERR(kernel_type);
if (IS_ERR(kernel_type))
goto out_type;
kernel_dev = copy_mount_string(dev_name);
ret = PTR_ERR(kernel_dev);
if (IS_ERR(kernel_dev))
goto out_dev;
options = copy_mount_options(data);
ret = PTR_ERR(options);
if (IS_ERR(options))
goto out_data;
// 2. do_mount 호출
ret = do_mount(kernel_dev, dir_name, kernel_type, flags, options);
// 3. 할당된 공간 해제
kfree(options);
out_data:
kfree(kernel_dev);
out_dev:
kfree(kernel_type);
out_type:
return ret;
}
✨ do_mount()
- fs/namespace.c, $3844
long do_mount(const char *dev_name, const char __user *dir_name,
const char *type_page, unsigned long flags, void *data_page)
{
struct path path;
int ret;
**// 1. 사용자 경로 -> 커널 내부 경로로 반환하기**
ret = **user_path_at(AT_FDCWD, dir_name, LOOKUP_FOLLOW, &path)**;
// 변환에 실패한 경우 리턴
if (ret)
return ret;
**// 2. 실질적 마운트 실행**
ret = **path_mount(dev_name, &path, type_page, flags, data_page)**;
**// 3. 해당 경로 자원 정리**
**path_put(&path)**;
return ret;
}
✨ user_path_at()
- 사용자 경로를 커널 내부 경로(구조체)로 변환
- fs/namei.c, $3066
int user_path_at(int dfd, const char __user *name, unsigned flags,
struct path *path)
{
**// 1. 파일명을 커널 공간으로 복사**
struct filename *filename = getname_flags(name, flags);
**// 2. 디렉터리 탐색**
// 이때 path 구조체에 mnt, dentry가 채워짐
int ret = filename_lookup(dfd, filename, flags, path, NULL);
**// 3. 자원 정리**
putname(filename);
return ret;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(user_path_at);
✨ path_mount()
- 주어진 경로를 통해 mount() 수행 ⇒ 디스패쳐 역할
- fs/namespace.c, $3765
- 마운트 유형을 판별 (remount, bind, move)
- 유형이 일치하지 않으면 일반 마운트 실행 (do_new_mount)
int path_mount(const char *dev_name, struct path *path,
const char *type_page, unsigned long flags, void *data_page)
{
unsigned int mnt_flags = 0, sb_flags;
int ret;
/* Discard magic */
if ((flags & MS_MGC_MSK) == MS_MGC_VAL)
flags &= ~MS_MGC_MSK;
/* Basic sanity checks */
if (data_page)
((char *)data_page)[PAGE_SIZE - 1] = 0;
if (flags & MS_NOUSER)
return -EINVAL;
ret = security_sb_mount(dev_name, path, type_page, flags, data_page);
if (ret)
return ret;
if (!may_mount())
return -EPERM;
if (flags & SB_MANDLOCK)
warn_mandlock();
/* Default to relatime unless overriden */
if (!(flags & MS_NOATIME))
mnt_flags |= MNT_RELATIME;
**// 1. 플래그 처리**
/* Separate the per-mountpoint flags */
if (flags & MS_NOSUID)
mnt_flags |= MNT_NOSUID;
if (flags & MS_NODEV)
mnt_flags |= MNT_NODEV;
if (flags & MS_NOEXEC)
mnt_flags |= MNT_NOEXEC;
if (flags & MS_NOATIME)
mnt_flags |= MNT_NOATIME;
if (flags & MS_NODIRATIME)
mnt_flags |= MNT_NODIRATIME;
if (flags & MS_STRICTATIME)
mnt_flags &= ~(MNT_RELATIME | MNT_NOATIME);
if (flags & MS_RDONLY)
mnt_flags |= MNT_READONLY;
if (flags & MS_NOSYMFOLLOW)
mnt_flags |= MNT_NOSYMFOLLOW;
/* The default atime for remount is preservation */
if ((flags & MS_REMOUNT) &&
((flags & (MS_NOATIME | MS_NODIRATIME | MS_RELATIME |
MS_STRICTATIME)) == 0)) {
mnt_flags &= ~MNT_ATIME_MASK;
mnt_flags |= path->mnt->mnt_flags & MNT_ATIME_MASK;
}
sb_flags = flags & (SB_RDONLY |
SB_SYNCHRONOUS |
SB_MANDLOCK |
SB_DIRSYNC |
SB_SILENT |
SB_POSIXACL |
SB_LAZYTIME |
SB_I_VERSION);
**// 2. 마운트 유형에 따른 함수 호출**
if ((flags & (MS_REMOUNT | MS_BIND)) == (MS_REMOUNT | MS_BIND))
return do_reconfigure_mnt(path, mnt_flags);
// 리마운트
if (flags & MS_REMOUNT)
return do_remount(path, flags, sb_flags, mnt_flags, data_page);
// 바인드 마운트
if (flags & MS_BIND)
return do_loopback(path, dev_name, flags & MS_REC);
if (flags & (MS_SHARED | MS_PRIVATE | MS_SLAVE | MS_UNBINDABLE))
return do_change_type(path, flags);
if (flags & MS_MOVE)
return do_move_mount_old(path, dev_name);
return **do_new_mount(path, type_page, sb_flags, mnt_flags, dev_name,
data_page)**;
}
✨ path_put()
- 해당 경로 자원 정리
void path_put(const struct path *path) { **// dentry 참조 해제** dput(path->dentry); **// mount 참조 해제** mntput(path->mnt); } EXPORT_SYMBOL(path_put);
✨ do_new_mount()
- 슈퍼 블록 로딩 및 VFS에 마운트 트리를 붙임
- fs/namespace.c. $3466
static int do_new_mount(struct path *path, const char *fstype, int sb_flags,
int mnt_flags, const char *name, void *data)
{
struct file_system_type *type;
struct fs_context *fc;
const char *subtype = NULL;
int err = 0;
if (!fstype)
return -EINVAL;
**// 1. 파일 시스템 탐색 (ext4, xfs 등)**
type = get_fs_type(fstype);
if (!type)
return -ENODEV;
if (type->fs_flags & FS_HAS_SUBTYPE) {
subtype = strchr(fstype, '.');
if (subtype) {
subtype++;
if (!*subtype) {
put_filesystem(type);
return -EINVAL;
}
}
}
**// 2. fs_context 구조체 할당**
fc = fs_context_for_mount(type, sb_flags);
put_filesystem(type);
if (IS_ERR(fc))
return PTR_ERR(fc);
/*
* Indicate to the filesystem that the mount request is coming
* from the legacy mount system call.
*/
fc->oldapi = true;
if (subtype)
err = vfs_parse_fs_string(fc, "subtype",
subtype, strlen(subtype));
if (!err && name)
err = vfs_parse_fs_string(fc, "source", name, strlen(name));
if (!err)
err = parse_monolithic_mount_data(fc, data);
if (!err && !mount_capable(fc))
err = -EPERM;
**// 3. 트리 생성**
if (!err)
err = **vfs_get_tree(fc)**;
if (!err)
err = **do_new_mount_fc(fc, path, mnt_flags)**;
**// 4. 자원 정리**
put_fs_context(fc);
return err;
}
✨ vfs_get_tree()
- 해당 파일 시스템 드라이버에게 슈퍼 블록을 세팅해달라고 요청하는 함수
- fs/super.c, $1803
- fc->ops->get_tree(fc) 호출 ⇒ ext4_get_tree(fc)
- 시스템 드라이버를 통해 슈퍼 블록 정보를 읽어오고 루트 디렉터리 메모리 생성
int vfs_get_tree(struct fs_context *fc)
{
struct super_block *sb;
int error;
// 중복 마운트 방지
if (fc->root)
return -EBUSY;
/* Get the mountable root in fc->root, with a ref on the root and a ref
* on the superblock.
*/
error = **fc->ops->get_tree(fc)**;
if (error < 0)
return error;
// 마운트 되어 있지 않으면 (슈퍼 노드 존재 X)
if (!fc->root) {
pr_err("Filesystem %s get_tree() didn't set fc->root, returned %i\n",
fc->fs_type->name, error);
/* We don't know what the locking state of the superblock is -
* if there is a superblock.
*/
BUG();
}
// root dentry에 접근해 슈퍼 블록 포인터를 가져옴
sb = fc->root->d_sb;
WARN_ON(!sb->s_bdi);
/*
* super_wake() contains a memory barrier which also care of
* ordering for super_cache_count(). We place it before setting
* SB_BORN as the data dependency between the two functions is
* the superblock structure contents that we just set up, not
* the SB_BORN flag.
*/
super_wake(sb, SB_BORN);
error = security_sb_set_mnt_opts(sb, fc->security, 0, NULL);
if (unlikely(error)) {
fc_drop_locked(fc);
return error;
}
/*
* filesystems should never set s_maxbytes larger than MAX_LFS_FILESIZE
* but s_maxbytes was an unsigned long long for many releases. Throw
* this warning for a little while to try and catch filesystems that
* violate this rule.
*/
WARN((sb->s_maxbytes < 0), "%s set sb->s_maxbytes to "
"negative value (%lld)\n", fc->fs_type->name, sb->s_maxbytes);
return 0;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(vfs_get_tree);
✨ do_new_mount_fc()
- 루트 dentry를 마운트 지점에 연결
- fs/namespace.c, $3425
static int do_new_mount_fc(struct fs_context *fc, struct path *mountpoint,
unsigned int mnt_flags)
{
struct vfsmount *mnt;
struct mountpoint *mp;
struct super_block *sb = fc->root->d_sb;
int error;
error = security_sb_kern_mount(sb);
if (!error && mount_too_revealing(sb, &mnt_flags))
error = -EPERM;
if (unlikely(error)) {
fc_drop_locked(fc);
return error;
}
// 슈퍼블록에 락 걸기
up_write(&sb->s_umount);
**// 1. 마운트 구조체 생성**
mnt = vfs_create_mount(fc);
if (IS_ERR(mnt))
return PTR_ERR(mnt);
mnt_warn_timestamp_expiry(mountpoint, mnt);
// 마운트 트리에 락 걸기
mp = lock_mount(mountpoint);
if (IS_ERR(mp)) {
mntput(mnt);
return PTR_ERR(mp);
}
**// 2. 트리 연결**
error = do_add_mount(real_mount(mnt), mp, mountpoint, mnt_flags);
unlock_mount(mp);
if (error < 0)
mntput(mnt);
return error;
}
✨ fc->ops->get_tree(fc)
- linux/fs_context.h, $90
fs_context_operations: 파일 시스템 드라이버 (여기서는 ext4)에서get_tree핸들러를 설정해둔 포인트- 마운트 시점에 fs_context를 생성할 때, get_tree가 드라이버에 의해 채워짐.
struct fs_context {
**const struct fs_context_operations *ops;**
struct mutex uapi_mutex; /* Userspace access mutex */
struct file_system_type *fs_type;
void *fs_private; /* The filesystem's context */
void *sget_key;
struct dentry *root; /* The root and superblock */
struct user_namespace *user_ns; /* The user namespace for this mount */
struct net *net_ns; /* The network namespace for this mount */
const struct cred *cred; /* The mounter's credentials */
struct p_log log; /* Logging buffer */
const char *source; /* The source name (eg. dev path) */
void *security; /* LSM options */
void *s_fs_info; /* Proposed s_fs_info */
unsigned int sb_flags; /* Proposed superblock flags (SB_*) */
unsigned int sb_flags_mask; /* Superblock flags that were changed */
unsigned int s_iflags; /* OR'd with sb->s_iflags */
enum fs_context_purpose purpose:8;
enum fs_context_phase phase:8; /* The phase the context is in */
bool need_free:1; /* Need to call ops->free() */
bool global:1; /* Goes into &init_user_ns */
bool oldapi:1; /* Coming from mount(2) */
bool exclusive:1; /* create new superblock, reject existing one */
};
struct fs_context_operations {
void (*free)(struct fs_context *fc);
int (*dup)(struct fs_context *fc, struct fs_context *src_fc);
int (*parse_param)(struct fs_context *fc, struct fs_parameter *param);
int (*parse_monolithic)(struct fs_context *fc, void *data);
**int (*get_tree)(struct fs_context *fc);**
int (*reconfigure)(struct fs_context *fc);
};
- 참고로, /fs/ext4/super.c에는 아래와 같이 기입되어 있음
static const struct fs_context_operations ext4_context_ops = {
.parse_param = ext4_parse_param,
**.get_tree = ext4_get_tree,**
.reconfigure = ext4_reconfigure,
.free = ext4_fc_free,
};
✨ ext4_get_tree()
- fs/ext4/super.c, $5763
static int ext4_get_tree(struct fs_context *fc)
{
return **get_tree_bdev(fc, ext4_fill_super)**;
}
✨ get_tree_bdev()
- 단일 블록 장치를 기반으로 슈퍼 블록 생성
- fs/super.c, $1655
int get_tree_bdev(struct fs_context *fc,
int (*fill_super)(struct super_block *,
struct fs_context *))
{
return get_tree_bdev_flags(fc, **fill_super**, 0);
}
✨ ext4_fill_super()
- 슈퍼 블록을 디스크에서 읽기 및 루트 디렉터리 inode 세팅
- 읽어온 데이터를 super_block *sb에 채워넣음
- fs/ext4/super.c, $5713
static int ext4_fill_super(struct super_block *sb, struct fs_context *fc)
{
struct ext4_fs_context *ctx = fc->fs_private;
struct ext4_sb_info *sbi;
const char *descr;
int ret;
sbi = ext4_alloc_sbi(sb);
if (!sbi)
return -ENOMEM;
fc->s_fs_info = sbi;
/* Cleanup superblock name */
strreplace(sb->s_id, '/', '!');
sbi->s_sb_block = 1; /* Default super block location */
if (ctx->spec & EXT4_SPEC_s_sb_block)
sbi->s_sb_block = ctx->s_sb_block;
// 디스크 읽기
ret = __ext4_fill_super(fc, sb);
if (ret < 0)
goto free_sbi;
if (sbi->s_journal) {
if (test_opt(sb, DATA_FLAGS) == EXT4_MOUNT_JOURNAL_DATA)
descr = " journalled data mode";
else if (test_opt(sb, DATA_FLAGS) == EXT4_MOUNT_ORDERED_DATA)
descr = " ordered data mode";
else
descr = " writeback data mode";
} else
descr = "out journal";
if (___ratelimit(&ext4_mount_msg_ratelimit, "EXT4-fs mount"))
ext4_msg(sb, KERN_INFO, "mounted filesystem %pU %s with%s. "
"Quota mode: %s.", &sb->s_uuid,
sb_rdonly(sb) ? "ro" : "r/w", descr,
ext4_quota_mode(sb));
/* Update the s_overhead_clusters if necessary */
ext4_update_overhead(sb, false);
return 0;
free_sbi:
ext4_free_sbi(sbi);
fc->s_fs_info = NULL;
return ret;
}
