[OS] open() 시스템 콜 분석
linux kernel sourse tree의 깃허브 코드를 참조해 시스템 콜 호출 시 변화 과정을 분석한 글입니다.
📌 open()
- 파일 또는 장치에 대한 접근을 초기화하는 데 사용되는 리눅스 시스템 콜
- open() 시스템 콜 호출 시
파일 디스크립터(file descriptor)를 반환하며, 이 디스크립터를 통해 이후의 파일 조작 (읽기, 쓰기 등)을 할 수 있다.
🫧 과정
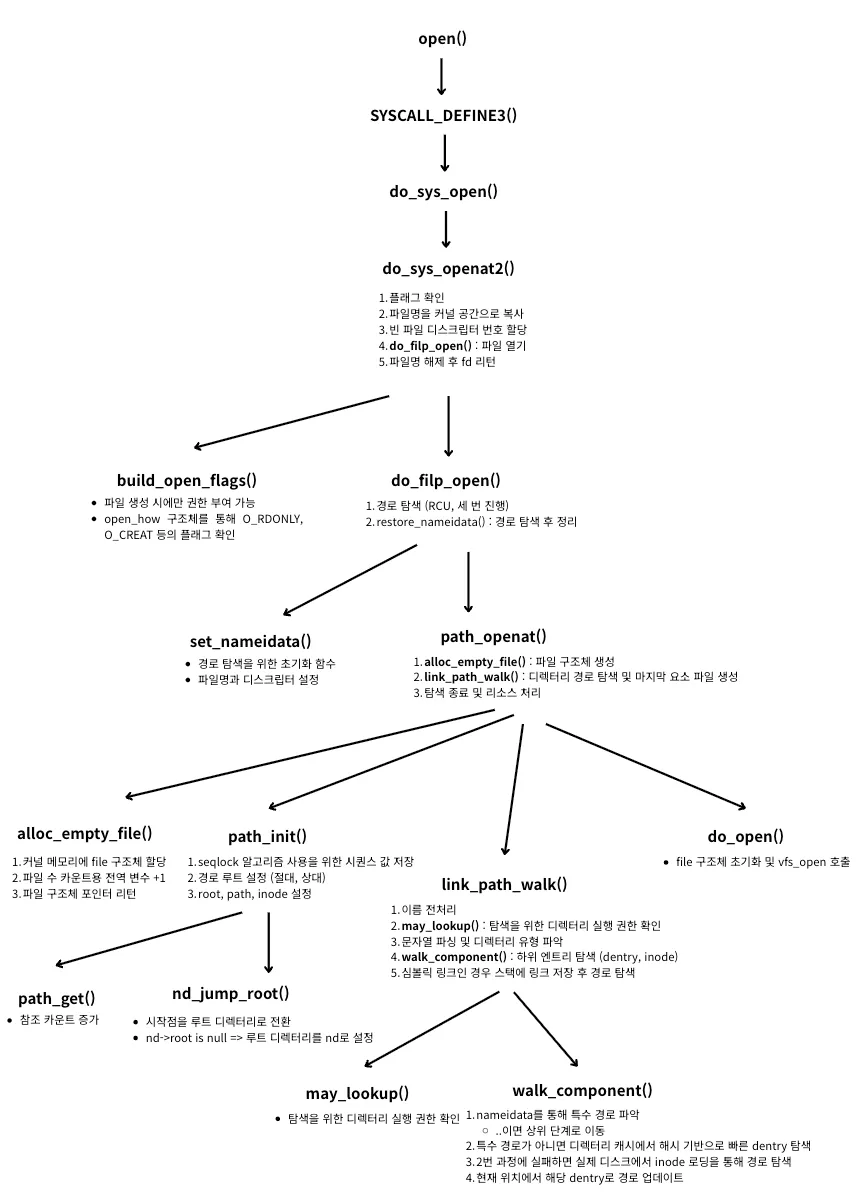
- 빈 파일 디스크립터 번호 할당
- 파일 구조체 생성 및 디렉터리 경로 탐색
- 마지막 요소 파일 구조체 생성 및 할당
🫧 특징
- 경로 탐색 과정에서 mount()와 동일한 함수 공유 (link_path_walk, restore_nameidata 등)
- 경로 탐색 과정에서 seqlock 알고리즘 사용
✨ seqlock 알고리즘
- 2.6 커널에 등장한 lock-free 동기화 메커니즘
- sequence counter을 통해 동기화 구현
- 스핀락, 쓰기 우선
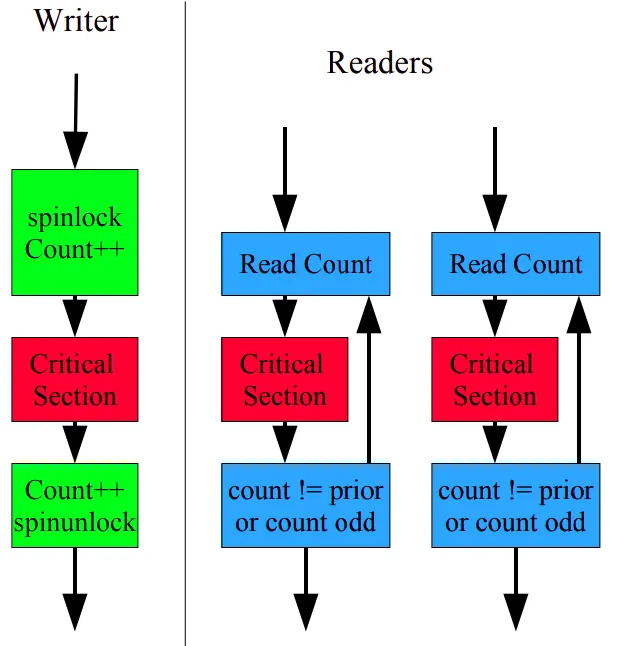
writer
- 들어갈 때 count++
- 나올 때도 count++
- 이를 통해 들어갈 때 홀수, 나올 때 짝수로 만듦.
reader
- CS에서 나오기 전과 후의 시퀀스 넘버를 확인함
- 일치하면&짝수이면 유효한 값
- 일치하지 않으면 다시 시도 (스핀락) ⇒ 이 때문에 간접적으로 공유 변수를 수정하는 RCU 알고리즘 사용
💡 왜 짝수인지 검사할까?
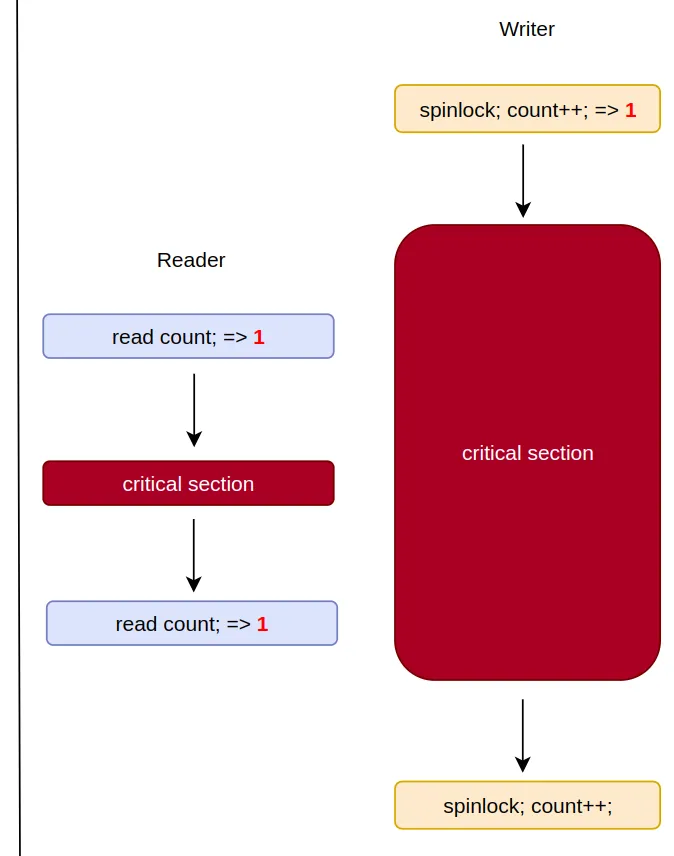
- 다음과 같은 상황을 방지하기 위함!
- writer가 먼저 홀수로 바꿨기 때문에 결과적으로 Reader은 무효
✨ seqlock vs RCU (Seqlock을 쓰는 경우)
- 데이터가 복잡 or 포인터가 아님
- 일반적으로 RCU는 포인터를 따라가며 탐색하므로 포인터가 아닌 경우 빠른 읽기를 위해 seqlock을 사용함
- 쓰기 경쟁이 적고 다시 읽을 수 있는 경우
- RCU는 쓰기 비용이 큼. (RCU에서 쓰기는 락을 걺)
- seqlock에서는 스핀락 + 시퀀스 번호 변경만 있으면 됨 - symlink도 파일 시스템 상에서는 dentry 객체로 표현
🫧 사용 예시 (코드)
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv) {
int fd = open("test", O_RDONLY); // 파일명, 모드
if (fd < 0) {
perror("Opening of the file is failed\n");
}
else {
printf("file sucessfully opened\n");
}
close(fd);
return 0;
}
🫧 코드
✨ SYSCALL_DEFINE3
- linux/fs/open.c, $1421
SYSCALL_DEFINE3(open, const char __user *, filename, int, flags, umode_t, mode)
{
if (force_o_largefile())
flags |= O_LARGEFILE;
return **do_sys_open(AT_FDCWD, filename, flags, mode)**;
}
✨ do_sys_open()
- linux/fs/open.c, $1414
long do_sys_open(int dfd, const char __user *filename, int flags, umode_t mode)
{
struct open_how how = build_open_how(flags, mode);
return **do_sys_openat2(dfd, filename, &how)**;
}
✨ do_sys_openat2()
-
디스크립터 번호 할당
-
linux/fs/open.c, $1386
static long do_sys_openat2(int dfd, const char __user *filename,
struct open_how *how)
{
struct open_flags op;
**// 1. 플래그 확인**
int fd = **build_open_flags(how, &op)**;
struct filename *tmp;
if (fd)
return fd;
**// 2. 파일명을 커널 공간으로 복사**
tmp = getname(filename);
if (IS_ERR(tmp))
return PTR_ERR(tmp);
**// 3. 빈 파일디스크립터 번호 할당**
fd = get_unused_fd_flags(how->flags);
if (fd >= 0) {
**// 4. 파일 열기**
struct file *f = **do_filp_open(dfd, tmp, &op)**;
if (IS_ERR(f)) {
put_unused_fd(fd);
fd = PTR_ERR(f);
} else {
fd_install(fd, f);
}
}
**// 5. 파일명 해제 후 fd 리턴**
putname(tmp);
return fd;
}
✨ build_open_flags()
-
플래그 설정
-
fs/open.c, $1202
// how : O_RDONLY, O_CREAT 등이 포함
inline int build_open_flags(const struct open_how *how, struct open_flags *op)
{
u64 flags = how->flags;
u64 strip = __FMODE_NONOTIFY | O_CLOEXEC;
int lookup_flags = 0;
int acc_mode = ACC_MODE(flags);
BUILD_BUG_ON_MSG(upper_32_bits(VALID_OPEN_FLAGS),
"struct open_flags doesn't yet handle flags > 32 bits");
/*
* Strip flags that either shouldn't be set by userspace like
* FMODE_NONOTIFY or that aren't relevant in determining struct
* open_flags like O_CLOEXEC.
*/
flags &= ~strip;
/*
* Older syscalls implicitly clear all of the invalid flags or argument
* values before calling build_open_flags(), but openat2(2) checks all
* of its arguments.
*/
if (flags & ~VALID_OPEN_FLAGS)
return -EINVAL;
if (how->resolve & ~VALID_RESOLVE_FLAGS)
return -EINVAL;
/* Scoping flags are mutually exclusive. */
if ((how->resolve & RESOLVE_BENEATH) && (how->resolve & RESOLVE_IN_ROOT))
return -EINVAL;
/* Deal with the mode. */
**// 파일 생성 시에만 권한 정보를 줄 수 있음 (퍼미션 비트)**
if (WILL_CREATE(flags)) {
if (how->mode & ~S_IALLUGO)
return -EINVAL;
op->mode = how->mode | S_IFREG;
} else {
if (how->mode != 0)
return -EINVAL;
op->mode = 0;
}
/*
* Block bugs where O_DIRECTORY | O_CREAT created regular files.
* Note, that blocking O_DIRECTORY | O_CREAT here also protects
* O_TMPFILE below which requires O_DIRECTORY being raised.
*/
if ((flags & (O_DIRECTORY | O_CREAT)) == (O_DIRECTORY | O_CREAT))
return -EINVAL;
/* Now handle the creative implementation of O_TMPFILE. */
if (flags & __O_TMPFILE) {
/*
* In order to ensure programs get explicit errors when trying
* to use O_TMPFILE on old kernels we enforce that O_DIRECTORY
* is raised alongside __O_TMPFILE.
*/
if (!(flags & O_DIRECTORY))
return -EINVAL;
if (!(acc_mode & MAY_WRITE))
return -EINVAL;
}
if (flags & O_PATH) {
/* O_PATH only permits certain other flags to be set. */
if (flags & ~O_PATH_FLAGS)
return -EINVAL;
acc_mode = 0;
}
/*
* O_SYNC is implemented as __O_SYNC|O_DSYNC. As many places only
* check for O_DSYNC if the need any syncing at all we enforce it's
* always set instead of having to deal with possibly weird behaviour
* for malicious applications setting only __O_SYNC.
*/
if (flags & __O_SYNC)
flags |= O_DSYNC;
op->open_flag = flags;
/* O_TRUNC implies we need access checks for write permissions */
if (flags & O_TRUNC)
acc_mode |= MAY_WRITE;
/* Allow the LSM permission hook to distinguish append
access from general write access. */
if (flags & O_APPEND)
acc_mode |= MAY_APPEND;
op->acc_mode = acc_mode;
op->intent = flags & O_PATH ? 0 : LOOKUP_OPEN;
if (flags & O_CREAT) {
op->intent |= LOOKUP_CREATE;
if (flags & O_EXCL) {
op->intent |= LOOKUP_EXCL;
flags |= O_NOFOLLOW;
}
}
if (flags & O_DIRECTORY)
lookup_flags |= LOOKUP_DIRECTORY;
if (!(flags & O_NOFOLLOW))
lookup_flags |= LOOKUP_FOLLOW;
if (how->resolve & RESOLVE_NO_XDEV)
lookup_flags |= LOOKUP_NO_XDEV;
if (how->resolve & RESOLVE_NO_MAGICLINKS)
lookup_flags |= LOOKUP_NO_MAGICLINKS;
if (how->resolve & RESOLVE_NO_SYMLINKS)
lookup_flags |= LOOKUP_NO_SYMLINKS;
if (how->resolve & RESOLVE_BENEATH)
lookup_flags |= LOOKUP_BENEATH;
if (how->resolve & RESOLVE_IN_ROOT)
lookup_flags |= LOOKUP_IN_ROOT;
if (how->resolve & RESOLVE_CACHED) {
/* Don't bother even trying for create/truncate/tmpfile open */
if (flags & (O_TRUNC | O_CREAT | __O_TMPFILE))
return -EAGAIN;
lookup_flags |= LOOKUP_CACHED;
}
op->lookup_flags = lookup_flags;
return 0;
}
✨ do_filp_open()
-
파일 경로 탐색 및 file 구조체 생성 함수
-
/fs/namei.c, $4006
// 디렉터리 파일 디스크립터, 경로, 설정
struct file *do_filp_open(int dfd, struct filename *pathname,
const struct open_flags *op)
{
// 탐색을 위한 구조체
struct nameidata nd;
int flags = op->lookup_flags;
struct file *filp;
**// 1. 경로 탐색 (RCU, 세 번의 탐색)**
**set_nameidata(&nd, dfd, pathname, NULL)**;
filp = **path_openat(&nd, op, flags | LOOKUP_RCU)**;
// 첫 번째 시도
if (unlikely(filp == ERR_PTR(-ECHILD)))
filp = path_openat(&nd, op, flags);
// 두 번째 시도
if (unlikely(filp == ERR_PTR(-ESTALE)))
filp = path_openat(&nd, op, flags | LOOKUP_REVAL);
// 경로 탐색 후 정리
restore_nameidata();
return filp;
}
✨ set_nameidata()
-
경로 탐색을 위한 초기화 함수 (파일명, 디스크립터 설정)
-
/fs/namei.c, $675
static inline void set_nameidata(struct nameidata *p, int dfd, struct filename *name,
const struct path *root)
{
**__set_nameidata(p, dfd, name)**;
p->state = 0;
if (unlikely(root)) {
p->state = ND_ROOT_PRESET;
p->root = *root;
}
}
✨ __set_nameidata()
-
초기화 및 파일 디스크립터 설정
-
/fs/namei.c, $660
static void __set_nameidata(struct nameidata *p, int dfd, struct filename *name)
{
struct nameidata *old = current->nameidata;
p->stack = p->internal;
p->depth = 0;
p->dfd = dfd;
p->name = name;
p->pathname = likely(name) ? name->name : "";
p->path.mnt = NULL; // 마운트 지점 초기화
p->path.dentry = NULL; // 디엔트리 초기화
p->total_link_count = old ? old->total_link_count : 0;
p->saved = old;
current->nameidata = p;
}
✨ path_openat()
-
구조체 할당 및 탐색
-
/fs/namei.c, $3977
static struct file *path_openat(struct nameidata *nd,
const struct open_flags *op, unsigned flags)
{
struct file *file;
int error;
**// 1. file 구조체 할당**
file = **alloc_empty_file(op->open_flag, current_cred())**;
if (IS_ERR(file))
return file;
if (unlikely(file->f_flags & __O_TMPFILE)) {
error = do_tmpfile(nd, flags, op, file);
} else if (unlikely(file->f_flags & O_PATH)) {
error = do_o_path(nd, flags, file);
} else {
const char *s = **path_init(nd, flags)**;
**// 2. 디렉터리 경로 탐색 및 마지막 요소 파일 생성/확인**
while (!(error = **link_path_walk(s, nd))** &&
// link_path_walk로 찾은 마지막 파일에 대한 기본 설정
(s = open_last_lookups(nd, file, op)) != NULL)
;
if (!error)
error = **do_open(nd, file, op)**;
**// 3. 탐색 종료 및 리소스 처리**
terminate_walk(nd);
}
if (likely(!error)) {
if (likely(file->f_mode & FMODE_OPENED))
return file;
WARN_ON(1);
error = -EINVAL;
}
fput(file);
if (error == -EOPENSTALE) {
if (flags & LOOKUP_RCU)
error = -ECHILD;
else
error = -ESTALE;
}
return ERR_PTR(error);
}
✨ alloc_empty_file()
-
파일 구조체 생성 함수
-
/fs/file_table.c, $210
struct file *alloc_empty_file(int flags, const struct cred *cred)
{
static long old_max;
struct file *f;
int error;
/*
* Privileged users can go above max_files
*/
if (get_nr_files() >= files_stat.max_files && !capable(CAP_SYS_ADMIN)) {
/*
* percpu_counters are inaccurate. Do an expensive check before
* we go and fail.
*/
if (percpu_counter_sum_positive(&nr_files) >= files_stat.max_files)
goto over;
}
**// 1. 커널 메모리에 file 구조체 할당**
f = kmem_cache_alloc(filp_cachep, GFP_KERNEL);
if (unlikely(!f))
return ERR_PTR(-ENOMEM);
error = init_file(f, flags, cred);
if (unlikely(error)) {
kmem_cache_free(filp_cachep, f);
return ERR_PTR(error);
}
**// 2. 파일 수를 카운트하는 전역 변수 ++;**
percpu_counter_inc(&nr_files);
**// 3. 파일 구조체 포인터 리턴**
return f;
over:
/* Ran out of filps - report that */
if (get_nr_files() > old_max) {
pr_info("VFS: file-max limit %lu reached\n", get_max_files());
old_max = get_nr_files();
}
return ERR_PTR(-ENFILE);
}
✨ path_init()
-
경로 탐색 시작점 결정 (절대 경로 상대 경로) - fs/namei.c, $2498
/* must be paired with terminate_walk() */
static const char *path_init(struct nameidata *nd, unsigned flags)
{
int error;
const char *s = nd->pathname;
/* LOOKUP_CACHED requires RCU, ask caller to retry */
// RCU 초기화
if ((flags & (LOOKUP_RCU | LOOKUP_CACHED)) == LOOKUP_CACHED)
return ERR_PTR(-EAGAIN);
if (!*s)
flags &= ~LOOKUP_RCU;
if (flags & LOOKUP_RCU)
rcu_read_lock();
else
nd->seq = nd->next_seq = 0;
nd->flags = flags;
nd->state |= ND_JUMPED;
// **1. seqlock 알고리즘 사용을 위해 시퀀스 값 저장**
nd->m_seq = __read_seqcount_begin(&mount_lock.seqcount);
nd->r_seq = __read_seqcount_begin(&rename_lock.seqcount);
smp_rmb();
// **2. 경로 루트 설정**
if (nd->state & ND_ROOT_PRESET) {
struct dentry *root = nd->root.dentry;
struct inode *inode = root->d_inode;
// dentry에 하위 디렉터리가 있는지 확인
if (*s && unlikely(!d_can_lookup(root)))
return ERR_PTR(-ENOTDIR);
nd->path = nd->root;
nd->inode = inode;
if (flags & LOOKUP_RCU) {
**// RCU + seqlock 함께 사용 => 빠르게 읽고, 유효성 검사 진행**
nd->seq = read_seqcount_begin(&nd->path.dentry->d_seq);
nd->root_seq = nd->seq;
} else {
**path_get(&nd->path)**;
}
return s;
}
nd->root.mnt = NULL;
/* Absolute pathname -- fetch the root (LOOKUP_IN_ROOT uses nd->dfd). */
**// 절대 경로**
if (*s == '/' && !(flags & LOOKUP_IN_ROOT)) {
**// 시작점을 루트 디렉터리로 전환**
error = **nd_jump_root(nd)**;
if (unlikely(error))
return ERR_PTR(error);
return s;
}
/* Relative pathname -- get the starting-point it is relative to. */
**// 상대 경로**
if (nd->dfd == AT_FDCWD) {
if (flags & LOOKUP_RCU) {
struct fs_struct *fs = current->fs;
unsigned seq;
do {
seq = read_seqcount_begin(&fs->seq);
nd->path = fs->pwd;
nd->inode = nd->path.dentry->d_inode;
nd->seq = __read_seqcount_begin(&nd->path.dentry->d_seq);
} while (read_seqcount_retry(&fs->seq, seq));
} else {
// 현재 작업 디렉터리
// 이때도 락 잡음
get_fs_pwd(current->fs, &nd->path);
// 디엔트리 따라가며 탐색
nd->inode = nd->path.dentry->d_inode;
}
} else {
/* Caller must check execute permissions on the starting path component */
CLASS(fd_raw, f)(nd->dfd);
struct dentry *dentry;
if (fd_empty(f))
return ERR_PTR(-EBADF);
if (flags & LOOKUP_LINKAT_EMPTY) {
if (fd_file(f)->f_cred != current_cred() &&
!ns_capable(fd_file(f)->f_cred->user_ns, CAP_DAC_READ_SEARCH))
return ERR_PTR(-ENOENT);
}
dentry = fd_file(f)->f_path.dentry;
if (*s && unlikely(!d_can_lookup(dentry)))
return ERR_PTR(-ENOTDIR);
nd->path = fd_file(f)->f_path;
if (flags & LOOKUP_RCU) {
nd->inode = nd->path.dentry->d_inode;
nd->seq = read_seqcount_begin(&nd->path.dentry->d_seq);
} else {
path_get(&nd->path);
nd->inode = nd->path.dentry->d_inode;
}
}
/* For scoped-lookups we need to set the root to the dirfd as well. */
if (flags & LOOKUP_IS_SCOPED) {
nd->root = nd->path;
if (flags & LOOKUP_RCU) {
nd->root_seq = nd->seq;
} else {
path_get(&nd->root);
nd->state |= ND_ROOT_GRABBED;
}
}
return s;
}
✨ path_get()
- 참조 카운트 증가
void path_get(const struct path *path)
{
mntget(path->mnt);
dget(path->dentry);
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(path_get);
✨ nd_jump_root()
-
시작점을 루트 디렉터리로 전환
-
/fs/namei.c, $1024
static int nd_jump_root(struct nameidata *nd)
{
if (unlikely(nd->flags & LOOKUP_BENEATH))
return -EXDEV;
if (unlikely(nd->flags & LOOKUP_NO_XDEV)) {
/* Absolute path arguments to path_init() are allowed. */
if (nd->path.mnt != NULL && nd->path.mnt != nd->root.mnt)
return -EXDEV;
}
if (!nd->root.mnt) {
// nd -> root가 비어있을 때 루트 디렉터리를 nd로 설정
int error = set_root(nd);
if (error)
return error;
}
if (nd->flags & LOOKUP_RCU) {
struct dentry *d;
nd->path = nd->root;
d = nd->path.dentry;
nd->inode = d->d_inode;
nd->seq = nd->root_seq;
if (read_seqcount_retry(&d->d_seq, nd->seq))
return -ECHILD;
} else {
path_put(&nd->path);
nd->path = nd->root;
path_get(&nd->path);
nd->inode = nd->path.dentry->d_inode;
}
nd->state |= ND_JUMPED;
return 0;
}
✨ link_path_walk()
-
dentry를 따라가며 경로 탐색 및 구성
-
/fs/namei.c, $2402
static int link_path_walk(const char *name, struct nameidata *nd)
{
int depth = 0; // depth <= nd->depth
int err;
nd->last_type = LAST_ROOT;
nd->flags |= LOOKUP_PARENT;
if (IS_ERR(name))
return PTR_ERR(name);
**// 1. 이름 전처리**
while (*name=='/')
name++;
if (!*name) {
nd->dir_mode = 0; // short-circuit the 'hardening' idiocy
return 0;
}
/* At this point we know we have a real path component. */
for(;;) {
struct mnt_idmap *idmap;
const char *link;
unsigned long lastword;
// 사용자 환경에 맞춘 id 재매핑(리마운트) 을 위해 필요 (ex, 컨테이너)
// https://lwn.net/Articles/837566/
idmap = mnt_idmap(nd->path.mnt);
**// 2. 탐색을 위한 디렉터리 실행 권한 확인**
err = **may_lookup(idmap, nd)**;
if (err)
return err;
nd->last.name = name;
name = hash_name(nd, name, &lastword);
**// 3. 문자열 파싱 및 디렉터리 유형 파악 (., .., 일반)**
switch(lastword) {
// ..
case LAST_WORD_IS_DOTDOT:
nd->last_type = LAST_DOTDOT;
nd->state |= ND_JUMPED;
break;
// .
case LAST_WORD_IS_DOT:
nd->last_type = LAST_DOT;
break;
default:
nd->last_type = LAST_NORM;
nd->state &= ~ND_JUMPED;
struct dentry *parent = nd->path.dentry;
if (unlikely(parent->d_flags & DCACHE_OP_HASH)) {
err = parent->d_op->d_hash(parent, &nd->last);
if (err < 0)
return err;
}
}
if (!*name)
goto OK;
/*
* If it wasn't NUL, we know it was '/'. Skip that
* slash, and continue until no more slashes.
*/
do {
name++;
} while (unlikely(*name == '/'));
if (unlikely(!*name)) {
OK:
/* pathname or trailing symlink, done */
// 스택이 비어 있다면 탐색 종료
.. 아니면 스택 --하고 해당 링크 재탐색
if (!depth) {
nd->dir_vfsuid = i_uid_into_vfsuid(idmap, nd->inode);
nd->dir_mode = nd->inode->i_mode;
nd->flags &= ~LOOKUP_PARENT;
return 0;
}
/* last component of nested symlink */
name = nd->stack[--depth].name;
**// 4. 하위 엔트리 탐색 (dentry, inode 탐색)**
link = **walk_component(nd, 0)**;
} else {
/* not the last component */
link = walk_component(nd, WALK_MORE);
}
**// 5. 심볼릭 링크인 경우 스택에 링크 저장 후 경로 탐색**
if (unlikely(link)) {
if (IS_ERR(link))
return PTR_ERR(link);
/* a symlink to follow */
nd->stack[depth++].name = name;
name = link;
continue;
}
if (unlikely(!d_can_lookup(nd->path.dentry))) {
if (nd->flags & LOOKUP_RCU) {
// RCU 일시중지
if (!try_to_unlazy(nd))
return -ECHILD;
}
return -ENOTDIR;
}
}
}
✨ may_lookup()
-
탐색을 위한 디렉터리 실행 권한 확인
-
fs/namei.c, $1813
static inline int may_lookup(struct mnt_idmap *idmap,
struct nameidata *restrict nd)
{
int err, mask;
// RCU 모드는 모든 블로킹을 피해야 하므로 검사하지 않는다는 MAY_NOT_BLOCK 플래그 추가
mask = nd->flags & LOOKUP_RCU ? MAY_NOT_BLOCK : 0;
// exec 권한 검사
err = inode_permission(idmap, nd->inode, mask | MAY_EXEC);
if (likely(!err))
return 0;
// If we failed, and we weren't in LOOKUP_RCU, it's final
if (!(nd->flags & LOOKUP_RCU))
return err;
// Drop out of RCU mode to make sure it wasn't transient
if (!try_to_unlazy(nd))
return -ECHILD; // redo it all non-lazy
if (err != -ECHILD) // hard error
return err;
return inode_permission(idmap, nd->inode, MAY_EXEC);
}
✨ walk_component()
-
경로 파악 및 dentry 탐색
-
/fs/namei.c, $2097
static const char *walk_component(struct nameidata *nd, int flags)
{
struct dentry *dentry;
/*
* "." and ".." are special - ".." especially so because it has
* to be able to know about the current root directory and
* parent relationships.
*/
**// 1. nameidata에 저장된 경로를 통해 ., .. 등의 특수 경로 파악**
if (unlikely(nd->last_type != LAST_NORM)) {
if (!(flags & WALK_MORE) && nd->depth)
put_link(nd);
**// 1-1. ..이면 상위 단계로 거슬러 올라가기**
return handle_dots(nd, nd->last_type);
}
**// 2. 특수 경로가 아니면 디렉터리 캐시에서 해시 기반으로 빠른 dentry 탐색 (디스크 I/O X)**
dentry = lookup_fast(nd);
if (IS_ERR(dentry))
return ERR_CAST(dentry);
**// 3. 2번 과정에 실패하면 실제 디스크에서 inode 로딩을 통해 경로 탐색**
if (unlikely(!dentry)) {
dentry = lookup_slow(&nd->last, nd->path.dentry, nd->flags);
if (IS_ERR(dentry))
return ERR_CAST(dentry);
}
if (!(flags & WALK_MORE) && nd->depth)
put_link(nd);
**// 4. 현재 위치에서 해당 dentry로 경로 업데이트**
return step_into(nd, flags, dentry);
}
✨ do_open()
- 실제 파일 열기 작업을 수행하는 함수
static int do_open(struct nameidata *nd,
struct file *file, const struct open_flags *op)
{
struct mnt_idmap *idmap;
int open_flag = op->open_flag;
bool do_truncate;
int acc_mode;
int error;
if (!(file->f_mode & (FMODE_OPENED | FMODE_CREATED))) {
error = complete_walk(nd);
if (error)
return error;
}
if (!(file->f_mode & FMODE_CREATED))
audit_inode(nd->name, nd->path.dentry, 0);
idmap = mnt_idmap(nd->path.mnt);
if (open_flag & O_CREAT) {
if ((open_flag & O_EXCL) && !(file->f_mode & FMODE_CREATED))
return -EEXIST;
if (d_is_dir(nd->path.dentry))
return -EISDIR;
error = may_create_in_sticky(idmap, nd,
d_backing_inode(nd->path.dentry));
if (unlikely(error))
return error;
}
if ((nd->flags & LOOKUP_DIRECTORY) && !d_can_lookup(nd->path.dentry))
return -ENOTDIR;
do_truncate = false;
acc_mode = op->acc_mode;
if (file->f_mode & FMODE_CREATED) {
/* Don't check for write permission, don't truncate */
open_flag &= ~O_TRUNC;
acc_mode = 0;
} else if (d_is_reg(nd->path.dentry) && open_flag & O_TRUNC) {
error = mnt_want_write(nd->path.mnt);
if (error)
return error;
do_truncate = true;
}
**// file 구조체 초기화 및 vfs_open**
error = may_open(idmap, &nd->path, acc_mode, open_flag);
if (!error && !(file->f_mode & FMODE_OPENED))
error = vfs_open(&nd->path, file);
if (!error)
error = security_file_post_open(file, op->acc_mode);
if (!error && do_truncate)
error = handle_truncate(idmap, file);
if (unlikely(error > 0)) {
WARN_ON(1);
error = -EINVAL;
}
if (do_truncate)
mnt_drop_write(nd->path.mnt);
return error;
}
